3GPP Access:
3GPP Access includes all the entities involved in the network are defined by 3GPP.
Example: A 3GPP defined UE getting access from 5G-RAN ( gNB ) and 5GC.

Non-3GPP Access:
Non-3GPP Access includes access from the entities those are not defined by 3GPP such as WLAN.
Non-3GPP access is further divided into 2 categories:
- Trusted Non-3GPP Access
- Untrusted Non-3GPP Access
Let’s understand more about both the categories in details.
- Untrusted Non-3GPP Access:
In Non-trusted access, the access point is not maintained and operated by the same operator of 5G network. N3IWF ( Non-3GPP Interworking Network Function) network function is introduced to get the access by interworking with 5G core network.
Following is the architecture attached for this access:
Key points addressing this above architecture:- IPSec secured connection is established between UE and N3IWF to provide security to control and data plane packets.
- EAP based Security algorithm is enabled to protect NAS messages.
- Another IPSec SA ( Security Association ) is establishment to transport user plane data.
- GRE ( Generic Routing Encapsulation ) protocol is used to carry user PDU between UE and N3IWF. GRE Protocol also ensures QoS models.
- Trusted Non-3GPP Access:
Trusted Access means that the operator of 5G Core Network is also in charge of operating and maintain the non-3GPP access point eg WIFI etc.
Following scenarios considered in 3GPP Release 16 and onwards for trusted Non-3GPP Access:
- Mobile Wireless Access:
- UE is Mobile with NAS Layer
- Access Point: Trusted Non-3GPP Access Point ( TNAP )
- Gateway Function: Trusted Non-3GPP Gateway Function ( TNGF )
- TNGF is in practice equivalent to N3IWF with the exception of using an IPSec tunnel with no encryption (lowering the UE CPU Load )
- WLAN security is forced between UE and TNAP

- Non-3GPP Mobile Wireless Access:
- UE is Mobile without NAS layer called as Non-5G Capable over WLAN ( N5CW )
- Access Point: Trusted Non-3GPP Access Point ( TNAP )
- Gateway Function: Trusted WLAN Interworking Function ( TWIF )
- TWIF convers UE messages and form NAS packet towards AMF, hereby TWIF works as 5G merged UE+RAN towards CN.

- Fixed Wireless Access:
- UE is Fixed with NAS layer called as 5G-RG.
- Wireless 5G-Access Network ( W5AN ) Function is defined in CN.
- W5AN includes Wireless Access Gateway Function which is equivalent to TNGF.

- Non-3GPP Fixed Wireless Access:
- UE is Fixed without NAS layer called as FN-RG.
- Wireless 5G-Access Network ( W5AN ) Function is defined in CN.
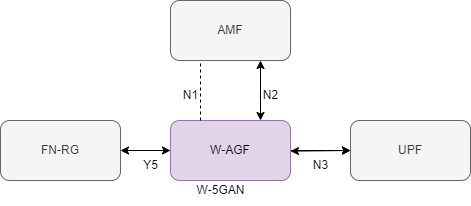
- Mobile Wireless Access:
NOTE: Further details on Fixed wireless Access is being added in 3GPP Rel 17 and onwards.
